Sound masking is the inclusion of generated sound (commonly, though inaccurately, referred to as “white noise” or “pink noise”) into an environment to mask unwanted sound. It relies on auditory masking.
Sound masking is ambient background sound engineered to match the frequency of human speech for greater speech privacy. Adding sound to a space actually makes the space seem quieter. It sounds counter-intuitive but it’s true.
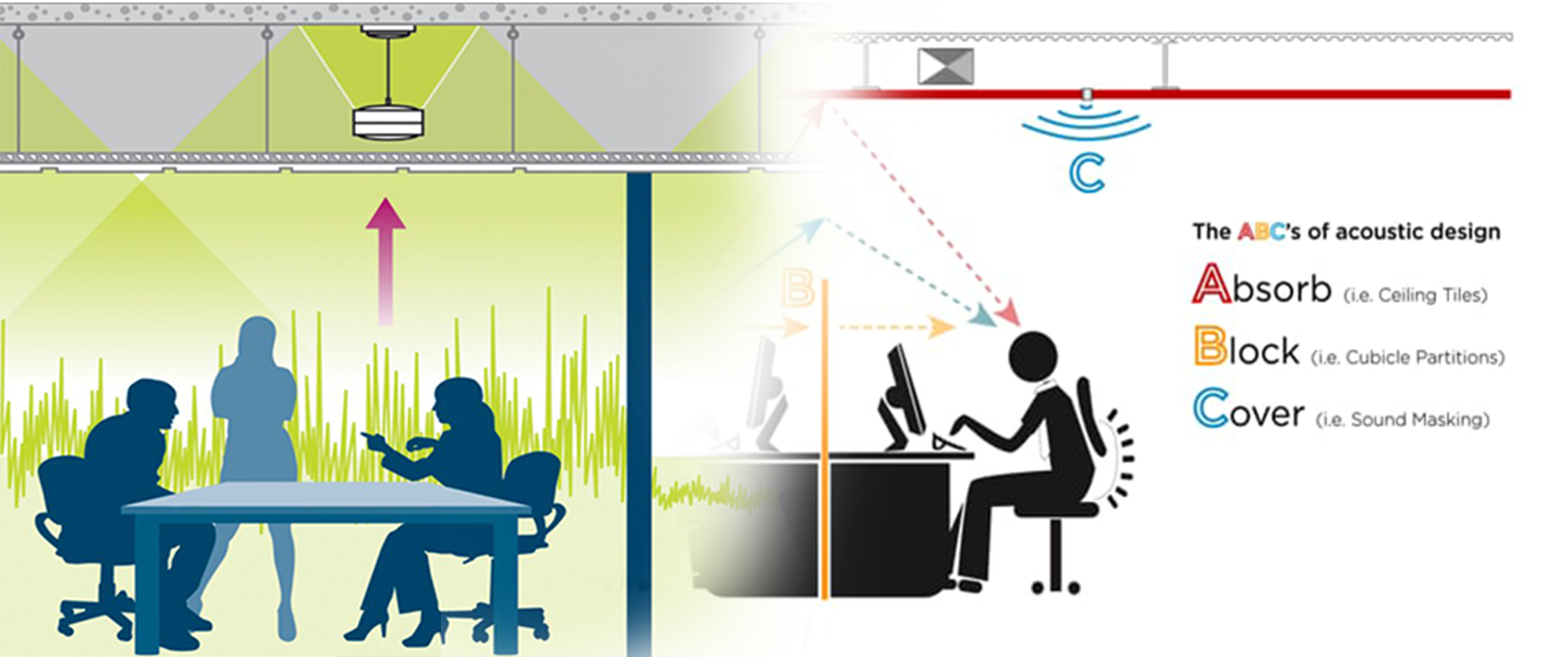
Sound masking is a technique used to reduce the perception of noise and increase privacy in an environment by adding a low-level, unobtrusive background sound. The purpose of sound masking is to make conversations and other noises less intelligible and distracting, creating a more comfortable and productive space. Here are some key points about sound masking:
It’s important to note that sound masking is different from noise cancellation or noise isolation. While noise cancellation aims to actively eliminate or neutralize external sounds, sound masking introduces a controlled background sound to reduce the impact of other noises. The effectiveness of sound masking depends on factors such as the design of the system, the ambient noise levels, and the specific requirements of the environment.